How Microbes Function
Understanding the Microbial Process
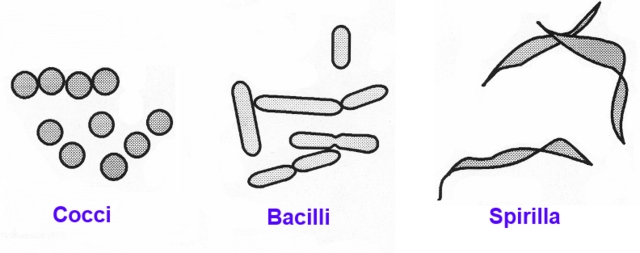
Bacteria feed by absorption through their cell membranes.
- Stage 1: Bacteria secrete extracellular enzymes that break down large particulates and solids. These enzymes are produced continuously.
- Stage 2: The reduced particles are absorbed through the outer membrane where additional cellular enzymes process them further.
- Stage 3: The particles then enter the inner cell, where enzymes complete the breakdown of organic matter.
This process results in the production of CO2 and H2O, while simultaneously seeding new bacteria through cell division. Time and oxygen availability are crucial when using bacterial inoculants for treatment.
Want to learn more?
Check out our SDS Documentation or contact us to learn more